1. About this Guide
This guide has been created to give a quick start to install active/active clustering in PacketFence 7+. This guide does not include advanced troubleshooting of the active/active clustering. Refer to the documentation of HAProxy and Keepalived for advanced features.
1.1. Other sources of information
- Developer’s Guide
-
Covers API, captive portal customization, application code customizations and instructions for supporting new equipment.
- Installation Guide
-
Covers installation and configuration of PacketFence.
- Network Devices Configuration Guide
-
Covers switches, WiFi controllers and access points configuration.
- Upgrade Guide
-
Covers compatibility related changes, manual instructions and general notes about upgrading.
NEWS.asciidoc-
Covers noteworthy features, improvements and bug fixes by release.
These files are included in the package and release tarballs.
2. Assumptions
- You have at least three (3) installed PacketFence (v7+) servers
- The servers are running one of RHEL / CentOS 7 / Debian 9
- The servers have identical identifiers for network interfaces (e.g. eth0)
- The servers network interfaces are on the same layer 2 network
- The servers must have IPv6 disabled.
3. Cluster Setup
3.1. Install the database replication tools
First, you will need to install, on each servers, Percona Xtrabackup for the synchronization to work correctly.
On RHEL / CentOS 7:
# yum install http://www.percona.com/downloads/percona-release/redhat/0.1-3/percona-release-0.1-3.noarch.rpm
Disable Percona repositories, so that installing software from that repository requires explicit action.
# sed -i 's/enabled = 1/enabled = 0/g' /etc/yum.repos.d/percona-release.repo# yum install percona-xtrabackup socat --enablerepo=percona-release-x86_64
apt-get install lsb-release
wget https://repo.percona.com/apt/percona-release_0.1-4.$(lsb_release -sc)_all.deb
dpkg -i percona-release_0.1-4.$(lsb_release -sc)_all.deb
apt-get update
apt-get -y install percona-xtrabackup-24For the next steps, you want to make sure that you didn’t configure anything in /usr/local/pf/conf/cluster.conf. If you already did, comment all the configuration in the file and do a configreload (/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd configreload hard).
3.2. Setup on the first server of your cluster
First, on the first server, start packetfence-mariadb and make sure it was able to start in 'standalone' mode.
# systemctl start packetfence-mariadb
Then, secure your installation
# mysql_secure_installation
Then, you will need to create a user for the database replication that PacketFence will use. You can use any username/password combination. After creating the user, keep its information close-by for usage in the configuration.
# mysql -u root -p
CREATE USER 'pfcluster'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'aMuchMoreSecurePassword';GRANT PROCESS, RELOAD, LOCK TABLES, REPLICATION CLIENT, SUPER ON *.* TO 'pfcluster'@'%';
CREATE USER 'pfcluster'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'aMuchMoreSecurePassword';GRANT PROCESS, RELOAD, LOCK TABLES, REPLICATION CLIENT, SUPER ON *.* TO 'pfcluster'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
3.3. The others Servers configuration
First, you need to make sure the interfaces name will be the same on all servers. See 'Setting the interfaces name on CentOS 7' in the Appendix section of this document if all your servers don’t already have the same interface names.
Next, you will need to configure each server so the services can bind on IP addresses they don’t currently have configured. This allows faster failover of the services.
On all your servers, add the following line in /etc/sysctl.conf and then reload with 'sysctl -p'
net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind = 1
3.3.1. Basic PacketFence configuration
Now, on the first server of your cluster, you should go through the configurator, until step 7 (Services). You should leave the services stopped at the end of the configurator.
Then restart PacketFence’s mariadb on the first server:
# systemctl restart packetfence-mariadb
On the other servers of your cluster, configure only the network interfaces (step 2) without going past that section in the configurator. If the other servers already have the right IP addresses configured on their interfaces, you can ignore this step.
At this point, for a VLAN enforcement configuration for example, the network interfaces of your servers must be configured, and you must be able to see, for each server:
In /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ |
|
One Management Interface |
ifcfg-YourFirstInterfaceName |
One Secondary Interface |
ifcfg-YourSecondInterfaceName |
One Registration Interface |
ifcfg-YourSecondInterfaceName.YourRegistrationVLANID |
One Isolation Interface |
ifcfg-YourSecondInterfaceName.YourIsolationVLANID |
3.4. Create the new cluster
3.4.1. PacketFence Configuration Modification
In /usr/local/pf/conf/pf.conf :
[database]host=127.0.0.1[active_active]# Change these 2 values by the credentials you've set when configuring MariaDB abovegalera_replication_username=pfclustergalera_replication_password=aMuchMoreSecurePassword
Then, in /usr/local/pf/conf/pfconfig.conf :
[mysql]host=127.0.0.1
Now, restart packetfence-config and reload the configuration. You will see errors related to a cache write issue but you can safely ignore it for now. These appear because packetfence-config cannot connect to the database yet.
# systemctl restart packetfence-config# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd configreload hard
3.4.2. Configure cluster.conf
In order to create a new cluster, you need to configure /usr/local/pf/conf/cluster.conf on the first server of your cluster.
You will need to configure it with your server hostname. Use : hostname command (without any arguments) to get it.
In the case of this example it will be 'pf1.example.com'.
The 'CLUSTER' section represents the virtual IP addresses of your cluster that will be shared by your servers.
In this example, eth0 is the management interface, eth1.2 is the registration interface and eth1.3 is the isolation interface.
On the first server, create a configuration similar to this :
[CLUSTER]management_ip=192.168.1.10[CLUSTER interface eth0]ip=192.168.1.10[CLUSTER interface eth1.2]ip=192.168.2.10[CLUSTER interface eth1.3]ip=192.168.3.10[pf1.example.com]management_ip=192.168.1.5[pf1.example.com interface eth0]ip=192.168.1.5[pf1.example.com interface eth1.2]ip=192.168.2.5[pf1.example.com interface eth1.3]ip=192.168.3.5[pf2.example.com]management_ip=192.168.1.6[pf2.example.com interface eth0]ip=192.168.1.6[pf2.example.com interface eth1.2]ip=192.168.2.6[pf2.example.com interface eth1.3]ip=192.168.3.6[pf3.example.com]management_ip=192.168.1.7[pf3.example.com interface eth0]ip=192.168.1.7[pf3.example.com interface eth1.2]ip=192.168.2.7[pf3.example.com interface eth1.3]ip=192.168.3.7
Once this configuration is done, reload the configuration and perform a checkup.
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd configreload hard# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd checkup
The reload and the checkup will complain about the unavailability of the database, which you can safely ignore for now. Most important is that you don’t see any cluster configuration related errors during the checkup.
Then make sure the PacketFence clustering services will be started at boot by running the following command on all of your servers.
# systemctl set-default packetfence-cluster
systemctl stop packetfence-mariadb and systemctl stop mariadb).Still on the first server, start MariaDB forcing it to create a new cluster.
# systemctl stop packetfence-mariadb# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd generatemariadbconfig# /usr/local/pf/sbin/pf-mariadb --force-new-cluster
Then, restart PacketFence to apply all your changes
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pf restart
If no error is found in the previous configuration, the previous restart of packetfence should have started keepalived and radiusd-loadbalancer along with the other services. If you have set up a mail server on your first server, you should have receive a mail from keepalived to inform you that your first server got Virtual IP (VIP) adresses.
You should now have service using the first server on the IP addresses defined in the 'CLUSTER' sections.
3.5. Integrating the two other nodes
/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pf stop) and restart the steps from here.packetfence-mariadb (systemctl stop packetfence-mariadb) and start it with the new cluster option so the servers can join (/usr/local/pf/sbin/pf-mariadb --force-new-cluster)Now, you will need to integrate your two other nodes in your cluster.
3.5.1. Webservices configuration
On the first server, configure your webservices username and password by adding the following in pf.conf:
[webservices]user=packetpass=fence
While you can set the username and password to any value, make sure to keep it safe as you will need it while initializing the cluster below.
And reload the config, then restart httpd.webservices on the first server:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd configreload hard# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service httpd.webservices restart
3.5.2. Sync the nodes
The following instructions have to be done on each server (second and third servers) that will be joined in the cluster.
Do (and make sure it completes without any errors):
# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/sync --from=192.168.1.5 --api-user=packet --api-password=fence
Where :
- '192.168.1.5' is the management IP of the first server node
- 'packet' is the webservices username you have configured on the first server node
- 'fence' is the webservices password you have configured on the first server node
On all your servers, make sure that 'iptables' is stopped:
# systemctl stop packetfence-iptables
Then, reload the configuration and start the webservices on these servers:
# systemctl restart packetfence-config# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd configreload# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service haproxy-db restart# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service httpd.webservices restart
Make sure that each server is binding to it’s own management address and the VIP address. If it’s not, verify the /usr/local/pf/conf/cluster.conf management interface configuration.
# netstat -nlp | grep 9090
3.5.3. MariaDB sync
First, ensure your MariaDB instance running with --force-new-cluster is still running on the first node, if its not, start it again.
Then, ensure packetfence-mariadb is stopped on the two servers that will be joined:
# systemctl stop packetfence-mariadb
Now, flush any MariaDB data you have on the two servers and restart packetfence-mariadb so that the servers join the cluster.
# rm -fr /var/lib/mysql/*
# systemctl restart packetfence-mariadb
Checking the MariaDB sync
In order to check the MariaDB sync, you can look at the status of the wsrep status values inside MariaDB.
MariaDB> show status like 'wsrep%';
Important variables:
- 'wsrep_cluster_status': Display whether or not the node is part of a primary view or not. A healthy cluster should always show as primary
- 'wsrep_incoming_addresses': The current members of the cluster. All the nodes of your cluster should be listed there.
- 'wsrep_local_state_comment': Current sync state of the cluster. A healthy state is 'Synced'. Refer to the Galera cluster documentation for the meaning of the other values this can have.
In order for the cluster to be considered healthy, all nodes must be listed under wsrep_incoming_addresses and wsrep_local_state_comment must be Synced. Otherwise look in the MariaDB log (/usr/local/pf/logs/mariadb_error.log)
Starting the first server normally
Once all servers are synced, go on the first server that should still be running with the --force-new-cluster option, break the command.
Now, start packetfence-mariadb normally and restart packetfence-iptables:
# systemctl restart packetfence-mariadb# systemctl restart packetfence-iptables
3.5.4. Wrapping up
Now restart PacketFence on all servers:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pf restart
Disable the access to the configurator by setting the currently-at file on each server:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd version > /usr/local/pf/conf/currently-at
Next, make sure to join domains through 'Configuration/Policies And Access Control/Domains/Active Directory Domains' on each node.
You should now reboot each server one by one waiting for the one you rebooted to come back online before proceeding to the next one. After each reboot, ensure the database sync is fine by performing the checks outlined in "Checking the MariaDB sync".
# reboot
3.6. Securing the cluster: Keepalived secret
From the PacketFence web administration interface, go in 'Configuration/System Configuration/Cluster' and change the 'Shared KEY'. Make sure you restart keepalived on all your servers using /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service keepalived restart
If you already use VRRP protocol on your network, you can also change the default 'Virtual Router ID' and enable 'VRRP Unicast'.
4. Understanding the Galera cluster synchronization
The Galera cluster stack used by PacketFence resembles a lot to how a normal MariaDB Galera cluster behaves but it contains hooks to auto-correct some issues that can occur.
/usr/local/pf/logs/mariadb_error.log4.1. Quorum behavior
A loss of quorum is when a server is not able to be part of a group that represents more than 50% of the configured servers in the cluster. This can occur if a node is isolated from a network perspective or if more than 50% of its peers aren’t alive (like in the case of a power outage).
The Galera cluster stack will continuously check that it has a quorum. Should one of the server be part of a group that doesn’t have the quorum in the cluster, it will put itself in read-only mode and stop the synchronization. During that time, your PacketFence installation will continue working but with some features disabled.
- RADIUS MAC Authentication: Will continue working and will return RADIUS attributes associated with the role that is registered in the database. If VLAN or RADIUS filters can apply to this device, they will but any role change will not be persisted.
- RADIUS 802.1X: Will continue working and if 'Dot1x recompute role from portal' is enabled, it will compute the role using the available authentication sources but will not save it in the database at the end of the request. If this parameter is disabled, it will behave like MAC Authentication. VLAN and RADIUS filters will still apply for the connections. If any of your sources are external (LDAP, AD, RADIUS, …), they must be available for the request to complete successfully.
- Captive portal: The captive portal will be disabled and display a message stating the system is currently experiencing an issue.
- DHCP listeners: The DHCP listeners will be disabled and packets will not be saved in the database. This also means Firewall SSO will not work during that time.
- Web administration interface: It will still be available in read-only mode for all sections and in read-write mode for the configuration section.
Once the server that is in read-only mode joins a quorum, it will go back in read-write mode and the system will go back to its normal behavior automatically.
4.2. Graceful shutdown behavior
When you are gracefully shutting down servers for a planned maintenance, you should always aim to leave a quorum alive so that once the server joins its peers again, it will always re-join the cluster gracefully. You can also leave only one of the nodes alive but keep in mind it will fall in read-only mode until all the nodes that were part of the last healthy quorum rejoin the cluster.
Should all your nodes shutdown gracefully, the last node to be shutdown will be the one that will be able to self-elect as master when you bring the machines back online. Bringing this node back online first is a best practice but not mandatory. In order to know which server would be able to self-elect as master, look for the node that has safe_to_bootstrap: 1 when executing the following command cat /var/lib/mysql/grastate.dat | grep 'safe_to_bootstrap:'.
4.3. Ungraceful shutdown behavior
/var/lib/mysql/gvwstate.dat exists on the node.If at least one node is still alive, other nodes will be able to connect to it and re-integrate the cluster.
When all nodes are ungracefuly shutdown, they will be able to recover when the last 2 running nodes will be able to talk to each other. If all nodes were shutdown at the same time, all of them must rejoin the cluster for it to form again. Until the cluster reaches a healthy state, you will not have any database service.
5. Troubleshooting a cluster
5.1. Recovering when a node is missing
If one of the nodes cannot recover, you can manually reset the cluster state. Note that this procedure is only valid if all the nodes were hard-shutdown at the same time.
First, stop packetfence-mariadb on all servers:
# systemctl stop packetfence-mariadb
Then remove /var/lib/mysql/gvwstate.dat on all the servers that are still alive.
Next, see the section 'Electing a new master' to start up a new cluster.
5.2. Electing a new master
At any time, you can start up a new cluster without the management node which is the source of truth by default. In order to do so, execute: /usr/local/pf/sbin/pf-mariadb --force-new-cluster.
Wait for another server to connect to this new cluster, break the command and start packetfence-mariadb like you normally would.
Note that if your management node is alive, but not communicating with the new master node, then it will create a new cluster on its side automatically unless it is in maintenance mode. When electing a new cluster, you should ensure your management has (or will have when its alive) valid communication with the newly promoted cluster. Otherwise, you will end up in a split brain situation. See 'Recovering from a split brain' to fix this.
5.3. Recovering from a split brain
If you leave the cluster in auto-recovery mode without electing a master manually, the structure of the cluster is made so that a split-brain can never occur since a server will fallback in read-only if it can’t join a primary view (quorum).
Should you decide to elect a new master and cause a split-brain for crash recovery purpose, you will have to wipe the data on all the servers that are part of one side of the split brain. This should be done once all the servers have re-gained communication.
5.4. Full recovery
If you want to perform a full recovery which can be necessary after experiencing an issue with Galera cluster, you must stop the node you wish to keep the data from and start it with the --force-new-cluster option. If this is not the case, you can continue onto the next step
# systemctl stop packetfence-mariadb# /usr/local/pf/sbin/pf-mariadb --force-new-cluster
5.4.1. On each of the discarded servers
First, stop packetfence-mariadb on all the servers you want to discard data from.
systemctl stop packetfence-mariadb
On each of the servers you want to discard the data from, you must destroy all the data in /var/lib/mysql and start packetfence-mariadb so it resyncs its data from scratch.
rm -fr /var/lib/mysql/*systemctl start packetfence-mariadb
You should then see /var/lib/mysql be populated again with the data and once MariaDB becomes available again on the server, it means the sync has completed. In case of issues, look in the MariaDB log file (/usr/local/pf/logs/mariadb_error.log)
--force-new-cluster command and start packetfence-mariadb normally. (systemctl start packetfence-mariadb)5.5. Putting a node in maintenance
When doing maintenance on a node (especially the management node), it is always better to put it in maintenance mode so it doesn’t try to join an existing cluster.
In order to activate the maintenance mode on a node:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/maintenance --activate
In order to deactivate the maintenance mode on a node:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/maintenance --deactivate
In order to see the current maintenance state on a node:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/maintenance
6. Maintenance and Operations
6.1. Shutting down a PacketFence Active/Active cluster of three nodes
As PacketFence cluster works in an active/active way, with statefull redundance, the order to stop the servers is not very important.
Example:
- Stop order: pf1 → pf2 → pf3
- Start order: pf3 → pf2 → pf1
Shutdown the servers:
- Logon to the first server with a SSH terminal
- Type the following command: shutdown -h now
- Logon to the next server, with a SSH terminal.
- Type the following command: ping IP_ADDRESS_OF_THE_FIRST_SERVER
- Once the server do not responce back, type the following command: shutdown -h now
- Proceed the same way with the last server.
6.2. Bringing up a PacketFence Active/Active cluster of three nodes
We want to bring up the cluster, as the same status it was before the shutdown.
Therefore, we will do the Shutting down procedure, but in reverse.
6.2.1. Bring up the "Last" server stopped
Start the server, logon to the SSH terminal and make a first checkup of the services:
packetfence-mariadb, type the command:
systemctl status packetfence-mariadb
Expected output:
[..]Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/packetfence-mariadb.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)Active: active (running) since ...[..]
packetFence-config, type the command:
systemctl status packetfence-config
Expected output:
[..]Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/packetfence-config.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)Active: active (running) since ...[..]
HAProxy, type the command:
systemctl status packetfence-haproxy-db
Expected output:
[..]Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/packetfence-haproxy-db.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)Active: active (running) since ...[..]
The server must now be ready.
6.2.2. Bring up the next server
Start the next server, logon to the SSH terminal.
Once prompted, check the packetFence-mariadb sync with the Master, type the command:
mysql -u root -pMariaDB> show status like 'wsrep%';
MariaDB [(none)]> show status like "wsrep%";+------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------+| Variable_name | Value |+------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------+...| wsrep_cluster_size | 2 |...| wsrep_connected | ON |...| wsrep_evs_state | OPERATIONAL |...| wsrep_local_state_comment | Synced |...+------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------+
Start the second slave, logon on terminal and go with a show status like 'wsrep%'; once again.
- The values must have changed to:
MariaDB [(none)]> show status like "wsrep%";+------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------+| Variable_name | Value |+------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------+...| wsrep_cluster_size | 3 |...| wsrep_evs_state | OPERATIONAL |...| wsrep_local_state_comment | Synced |...+------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------+
6.3. Backup procedure
6.3.1. Automatic Backup files
The PacketFence servers have a daily backup done, each night (0:30AM).
If you need to externalize those backups, they are in:
/root/backup
Files description:
-
packetfence-db-dump-innobackup-DATE_00h30.xbstream.gzare the SQL dump of your MariaDB database. -
packetfence-files-dump-DATE_00h30.tgzare the dump of the PacketFence files.
6.3.2. Manual backups
In case you need to make a "manual" backup, you can type the following command:
/usr/local/pf/addons/backup-and-maintenance.sh
As the daily automatic backups, you will find the files in:
/root/backup/
Two files will be available, tagged with the Date and Time of your backup.
7. Layer 3 clusters
PacketFence supports having clusters where servers are located in multiple layer 3 networks which we will also refer as cluster zones.
Simple RADIUS only clusters are more simple and can be configured without too much in-depth knowledge, but if you want to use the captive portal with a layer 3 cluster, this will definitely make your setup more complex and will certainly require a lot of thinking and understanding on how PacketFence works to be able to know how to properly design a cluster like this.
This section will describe the changes to do on your cluster.conf when dealing with layer 3 clusters but doesn’t cover all the cluster installation. In order to install your cluster, follow the instructions in "Cluster Setup" and refer to this section when reaching the step to configure your cluster.conf.
7.1. Simple RADIUS only cluster
In order to configure a RADIUS only layer 3 cluster, you will need at least 3 servers (5 are used in this example) with a single interface (used for management).
Cluster design and behavior:
- This example will use 3 servers in a network (called DC1), and 2 in another network (called DC2).
- Each group of server (in the same L2 network) will have a virtual IP address and will perform load-balancing to members in the same L2 zone (i.e. same network).
- All the servers will use MariaDB Galera cluster and will be part of the same database cluster meaning all servers will have the same data.
- In the event of the loss of DC1 or a network split between DC1 and DC2, the databases on DC2 will go in read-only and will exhibit the behavior described in "Quorum behavior".
- All the servers will share the same configuration and same cluster.conf. The data in cluster.conf will serve as an overlay to the data in pf.conf to perform changes specific to each layer 3 zone.
Things to take into consideration while performing the cluster setup:
- While going through the configurator to configure the network interfaces, you only need to have a single interface and set its type to management and high-availability.
Cluster configuration
When you are at the step where you need to configure your cluster.conf during the cluster setup, refer to the example below to build your cluster.conf.
[general]multi_zone=enabled[DC1 CLUSTER]management_ip=192.168.1.10[DC1 CLUSTER interface ens192]ip=192.168.1.10[DC1 pf1-dc1.example.com]management_ip=192.168.1.11[DC1 pf1-dc1.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.1.11[DC1 pf2-dc1.example.com]management_ip=192.168.1.12[DC1 pf2-dc1.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.1.12[DC1 pf3-dc1.example.com]management_ip=192.168.1.13[DC1 pf3-dc1.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.1.13[DC2 CLUSTER]management_ip=192.168.2.10[DC2 CLUSTER interface ens192]ip=192.168.2.10[DC2 pf1-dc2.example.com]management_ip=192.168.2.11[DC2 pf1-dc2.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.2.11[DC2 pf2-dc2.example.com]management_ip=192.168.2.12[DC2 pf2-dc2.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.2.12
Notes on the configuration:
- The hostnames (pf1-dc1.example.com, pf2-dc1.example.com, etc) are not directly related to the cluster logic and the servers can have any hostname without impacting the cluster behavior. The assignment of a server to a cluster zone is made by the first part of the section name (ex: "DC1 pf.example.com" assigns server "pf.example.com" to cluster zone "DC1")
- Each cluster zone needs to have its own "CLUSTER" definition that declares the virtual IPs to use for this cluster zone. This also declares the management IP on which the zone should be joined.
- Given your zones aren’t in the same layer 2 network, you cannot use the same virtual IP between your zones.
- You should always declare a "CLUSTER" definition even though a zone has only a single server.
- Your network equipment should point RADIUS authentication and accounting to both virtual IPs (192.168.1.10 and 192.168.2.10 in this example) either in primary/secondary or load-balancing mode.
- RFC3576 servers (CoA and RADIUS disconnect) should be declared on your network equipment (if supported) for both virtual IPs (192.168.1.10 and 192.168.2.10 in this example)
7.2. RADIUS server with captive-portal
In order to configure a RADIUS server with a captive-portal on a layer 3 cluster, you will need at least 3 servers (5 are used in this example) with 2 interfaces (one for management and one for registration).
Cluster design and behavior:
- This example will use 3 servers in a network (called DC1), and 2 in another network (called DC2).
- Each group of server (in the same L2 network) will have a virtual IP address and will perform load-balancing (RADIUS, HTTP) to members in the same L2 zone (i.e. same network).
- All the servers will use MariaDB Galera cluster and will be part of the same database cluster meaning all servers will have the same data.
- In the event of the loss of DC1 or a network split between DC1 and DC2, the databases on DC2 will go in read-only and will exhibit the behavior described in "Quorum behavior".
- All the servers will share the same configuration and same cluster.conf. The data in cluster.conf will serve as an overlay to the data in pf.conf and networks.conf to perform changes specific to each layer 3 zone.
The schema below presents the routing that needs to be setup in your network in order to deploy this example:
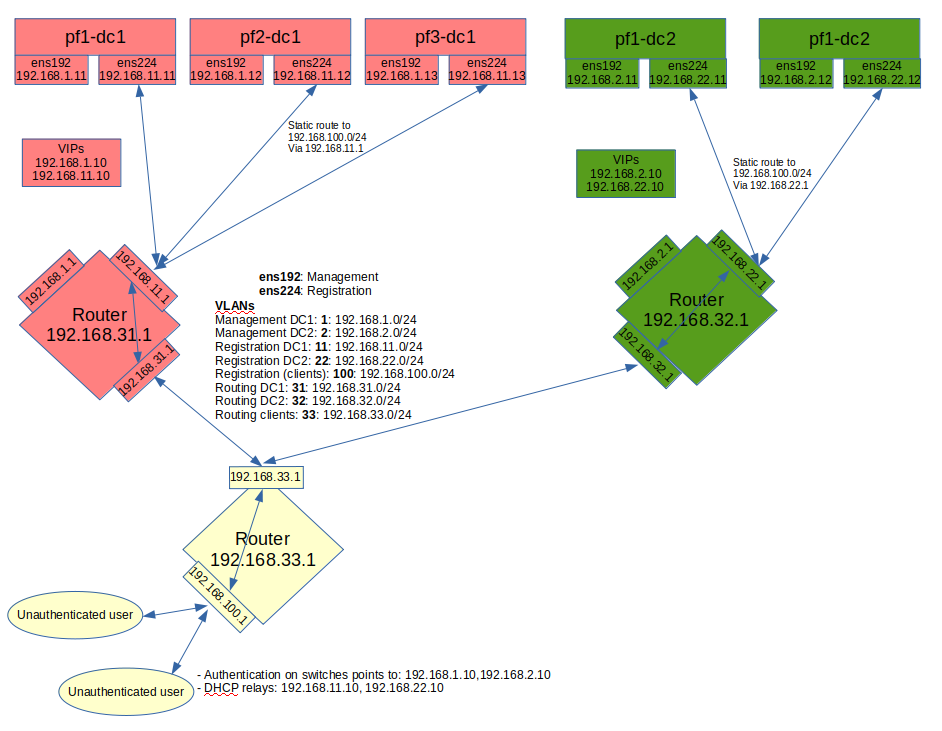
Notes on the schema:
- The static routes from the PacketFence servers to the gateways on your network equipment will be configured through networks.conf and do not need to be configured manually on the servers. You will simply need to declare the remote networks so that PacketFence offers DHCP on them and routes them properly.
- Since the network of the clients is not directly connected to the PacketFence servers via layer 2, you will need to use IP helper (DHCP relaying) on your network equipment that points to both virtual IPs of your cluster.
- We assume that your routers are able to route all the different networks that are involved for registration (192.168.11.0/24, 192.168.22.0/24, 192.168.100.0/24) and that any client in these 3 networks can be routed to any of these networks via its gateway (192.168.11.1, 192.168.22.2, 192.168.100.1).
- Access lists should be put in place to restrict the clients (network 192.168.100.0/24) from accessing networks other than the 3 registrations networks.
- No special routing is required for the management interface.
Things to take into consideration while performing the cluster setup:
- While going through the configurator to configure the network interfaces, you will need to set an interface to management and high-availability.
- While going through the configurator to configure the network interfaces, you will need to set an interface to registration.
Cluster configuration
When you are at the step where you need to configure your cluster.conf during the cluster setup, refer to the example below to build your cluster.conf.
[general]multi_zone=enabled[DC1 CLUSTER]management_ip=192.168.1.10[DC1 CLUSTER interface ens192]ip=192.168.1.10[DC1 CLUSTER interface ens224]ip=192.168.11.10[DC1 pf1-dc1.example.com]management_ip=192.168.1.11[DC1 pf1-dc1.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.1.11[DC1 pf1-dc1.example.com interface ens224]ip=192.168.11.11[DC1 pf2-dc1.example.com]management_ip=192.168.1.12[DC1 pf2-dc1.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.1.12[DC1 pf2-dc1.example.com interface ens224]ip=192.168.11.12[DC1 pf3-dc1.example.com]management_ip=192.168.1.13[DC1 pf3-dc1.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.1.13[DC1 pf3-dc1.example.com interface ens224]ip=192.168.11.13[DC2 CLUSTER]management_ip=192.168.2.10[DC2 CLUSTER interface ens192]ip=192.168.2.10[DC2 CLUSTER interface ens224]ip=192.168.22.10[DC2 pf1-dc2.example.com]management_ip=192.168.2.11[DC2 pf1-dc2.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.2.11[DC2 pf1-dc2.example.com interface ens224]ip=192.168.22.11[DC2 pf2-dc2.example.com]management_ip=192.168.2.12[DC2 pf2-dc2.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.2.12[DC2 pf2-dc2.example.com interface ens224]ip=192.168.22.12
Notes on the configuration:
- The hostnames (pf1-dc1.example.com, pf2-dc1.example.com, etc) are not directly related to the cluster logic and the servers can have any hostname without impacting the cluster behavior. The assignment of a server to a cluster zone is made by the first part of the section name (ex: "DC1 pf.example.com" assigns server "pf.example.com" to cluster zone "DC1")
- Each cluster zone needs to have its own "CLUSTER" definition that declares the virtual IPs to use for this cluster zone. This also declares the management IP on which the zone should be joined.
- Given your zones aren’t in the same layer 2 network, you cannot use the same virtual IP between your zones.
- You should always declare a "CLUSTER" definition even though a zone has only a single server.
- Your network equipment should point RADIUS authentication and accounting to both virtual IPs (192.168.1.10 and 192.168.2.10 in this example) either in primary/secondary or load-balancing mode.
- RFC3576 servers (CoA and RADIUS disconnect) should be declared on your network equipment (if supported) for both virtual IPs (192.168.1.10 and 192.168.2.10 in this example)
Servers network configuration
After you’ve finished configuring your cluster, on one of the servers, add the following in cluster.conf in order to configure both zones registration networks:
[DC1 CLUSTER network 192.168.11.0]dns=192.168.11.10split_network=disableddhcp_start=192.168.11.10gateway=192.168.11.10domain-name=vlan-registration.example.comnat_enabled=disablednamed=enableddhcp_max_lease_time=30fake_mac_enabled=disableddhcpd=enableddhcp_end=192.168.11.246type=vlan-registrationnetmask=255.255.255.0dhcp_default_lease_time=30
[DC2 CLUSTER network 192.168.22.0]dns=192.168.22.10split_network=disableddhcp_start=192.168.22.10gateway=192.168.22.10domain-name=vlan-registration.example.comnat_enabled=disablednamed=enableddhcp_max_lease_time=30fake_mac_enabled=disableddhcpd=enableddhcp_end=192.168.22.246type=vlan-registrationnetmask=255.255.255.0dhcp_default_lease_time=30
Client network configuration
Now, add the following in networks.conf in order to declare the common parameters for the clients in both zones
[192.168.100.0]gateway=192.168.100.1dhcp_start=192.168.100.20domain-name=vlan-registration.example.comnat_enabled=0named=enableddhcp_max_lease_time=30dhcpd=enabledfake_mac_enabled=disablednetmask=255.255.255.0type=vlan-registrationdhcp_end=192.168.100.254dhcp_default_lease_time=30
Then, to complete the client network configuration, you will need to override the next hop (route to reach the network) and DNS server in cluster.conf by adding the following:
[DC1 CLUSTER network 192.168.100.0]next_hop=192.168.11.1dns=192.168.11.10
[DC2 CLUSTER network 192.168.100.0]next_hop=192.168.22.1dns=192.168.22.10
Synchronization and wrapping-up
Then, reload the configuration and sync the cluster from the server on which you’ve performed the configuration:
/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd configreload hard/usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/sync --as-master
You should now restart PacketFence on all servers using:
/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pf restart
7.3. Remote MariaDB slave server
In cluster layer3 configuration you can configure a remote MariaDB server in slave mode. This will allow the primary database to be replicated from the central DC to the remote site. In normal operation the remote server will use the main sites database. However, when the link is broken the remote server will fallback and use its own local database in read-only mode.
For this configuration at least 3 servers are needed at the main site and at least 1 server is needed at the remote site.
Prepare the configuration
To configure PacketFence first turn ON "Master/Slave mode" in Configuration → System Configuration → Database → Advanced.
Next configure cluster.conf during the initial cluster setup, refer to the example below.
[general]multi_zone=enabled[DC1 CLUSTER]management_ip=192.168.1.10[DC1 CLUSTER interface ens192]ip=192.168.1.10mask=255.255.255.0type=management[DC1 CLUSTER interface ens224]ip=192.168.11.10mask=255.255.255.0enforcement=vlantype=internal[DC1 pf1-dc1.example.com]management_ip=192.168.1.11[DC1 pf1-dc1.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.1.11mask=255.255.255.0type=management[DC1 pf1-dc1.example.com interface ens224]ip=192.168.11.11mask=255.255.255.0enforcement=vlantype=internal[DC1 pf2-dc1.example.com]management_ip=192.168.1.12[DC1 pf2-dc1.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.1.12mask=255.255.255.0type=management[DC1 pf2-dc1.example.com interface ens224]ip=192.168.11.12mask=255.255.255.0enforcement=vlantype=internal[DC1 pf3-dc1.example.com]management_ip=192.168.1.13[DC1 pf3-dc1.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.1.13mask=255.255.255.0type=management[DC1 pf3-dc1.example.com interface ens224]ip=192.168.11.13mask=255.255.255.0enforcement=vlantype=internal[DC2 CLUSTER]management_ip=192.168.2.10masterslavemode=SLAVEmasterdb=DC1[DC2 CLUSTER interface ens192]ip=192.168.2.10mask=255.255.255.0type=management[DC2 CLUSTER interface ens224]ip=192.168.22.10mask=255.255.255.0enforcement=vlantype=internal[DC2 pf1-dc2.example.com]management_ip=192.168.2.11[DC2 pf1-dc2.example.com interface ens192]ip=192.168.2.11mask=255.255.255.0type=management[DC2 pf1-dc2.example.com interface ens224]ip=192.168.22.11mask=255.255.255.0enforcement=vlantype=internal
Note that in the DC2 CLUSTER section we defined this 2 values:
masterslavemode=SLAVEmasterdb=DC1
This mean that the cluster will be in SLAVE mode and will use the db of the DC1 cluster.
And we MUST defined the type and the enforcement on all the interfaces.
Prepare and start the master/slave replication
In order to setup the master a recent backup is required. Backups created prior to the inclusion of this feature will not work. Recent backups now include the replication runtime position of the binary logfile. First restart packetfence-mariadb on all of the servers in the main cluster.
systemctl restart packetfence-mariadb
Run the /usr/local/pf/addons/backup-and-maintenance.sh script on the master node of the main cluster. If you do not know which server is the master run this command on all nodes in the main cluster and only the master will create a backup file (eg: /root/backup/packetfence-db-dump-innobackup-YYYY-MM-DD_HHhss.xbstream.gz). Transfer this file to the remote server (eg: /root/backup/)
Connect to the remote server and perform the following to sync the configuration from the master cluster:
/usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/sync --from=192.168.1.11 --api-user=packet --api-password=fence/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd configreload hard
Then the following command to import the backup:
mkdir /root/backup/restorecd /root/backup/restorecp ../packetfence-db-dump-innobackup-YYYY-MM-DD_HHhss.xbstream.gz .gunzip packetfence-db-dump-innobackup-YYYY-MM-DD_HHhss.xbstream.gzxbstream -x < packetfence-db-dump-innobackup-YYYY-MM-DD_HHhss.xbstreammv packetfence-db-dump-innobackup-YYYY-MM-DD_HHhss.xbstream ../innobackupex --apply-log ./systemctl stop packetfence-mariadbrm -fr /var/lib/mysql/*mv * /var/lib/mysqlchown -R mysql: /var/lib/mysqlsystemctl start packetfence-mariadb
Lastly, run the following script on the remote server to start the slave replication.
/usr/local/pf/addons/makeslave.pl
Enter the MySQL root password: passwordEnter the MySQL master ip address: 192.168.1.11
The "MySQL master ip address" is the ip address of the master server where you created the backup file. Not the VIP of the primary cluster.
In the case when you run the script you have the following message:
ERROR 1045 (28000) at line 1: Access denied for user 'root'@'%' (using password: YES)Unable to grant replication on user pfcluster at ./addons/makeslave.pl line 42, <STDIN> line 2.
Then you need to be sure that the root user exist in the remote database and have the correct permissions (SELECT and GRANT):
SELECT * FROM mysql.user WHERE User='root' and host ='%'\GGRANT GRANT OPTION ON *.* TO root@'%' identified by 'password';GRANT SELECT ON *.* TO root@'%' identified by 'password';
Alternatively, to start the slave manually refer to the following:
Edit the file /var/lib/mysql/xtrabackup_binlog_info and note the file name and the position:
mariadb-bin.000014 7473
On the master server of the main cluster - where the backup was created - run the following command:
mysql -uroot -p -e "SELECT BINLOG_GTID_POS('mariadb-bin.000014', 7473)"
+---------------------------------------------+| BINLOG_GTID_POS('mariadb-bin.000014', 7473) |+---------------------------------------------+| 22-2-10459 |+---------------------------------------------+
mysql -uroot -pMariaDB [(none)]> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'pfcluster'@'%';MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
On the remote site master server run the following MySQL command as root:
SET GLOBAL gtid_slave_pos = '22-2-10459';CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='192.168.1.11', MASTER_PORT=3306, MASTER_USER='pfcluster', MASTER_PASSWORD='clusterpf', MASTER_USE_GTID=slave_pos;START SLAVE;
The replication MASTER_USER and MASTER_PASSWORD can be found in the main sites pf.conf. The MASTER_HOST is the ip address of the master server on the main site - where the backup was created. Do not use the VIP.
At the end it you want to check the status of the slave server for debug purposes you can run the follwing command:
SHOW SLAVE STATUS;
8. Advanced configuration
8.1. Removing a server from the cluster
First, you will need to stop PacketFence on your server and put it offline:
/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pf stopshutdown -h now
Then you need to remove all the configuration associated to the server from /usr/local/pf/conf/cluster.conf on one of the remaining nodes.
Configuration for a server is always prefixed by the server’s hostname.
Once you have removed the configuration, you need to reload it and synchronize it with the remaining nodes in the cluster.
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd configreload hard# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/sync --as-master
Now restart PacketFence on all the servers so that the removed node is not part of the clustering configuration.
Note that if you remove a node and end up having an even number of servers, you will get unexpected behaviors in MariaDB. You should always aim to have an odd number of servers at all time in your cluster.
8.2. Resynchronizing the configuration manually
If you did a manual change in a configuration file, an additional step is now needed.
In order to be sure the configuration is properly synced on all nodes, you will need to enter this command on the previously selected master node.
# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/sync --as-master
8.3. Adding files to the synchronization
In the event that you do modifications to non-synchronized files like switch modules, files in raddb/, etc, you can add those files to be synchronized when using /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/sync.
On one of the nodes, create /usr/local/pf/conf/cluster-files.txt
Add the additional files one per line in this file. We advise you add this file to the synchronization too.
Example :
/usr/local/pf/conf/cluster-files.txt/usr/local/pf/raddb/modules/mschap
8.4. HAProxy dashboard
You have the possibility to configure the HAProxy dashboard on each node which will give you statistics about the current state of your cluster.
Configuration is done in /usr/local/pf/conf/haproxy-portal.conf:
listen statsbind %%management_ip%%:1025mode httptimeout connect 10stimeout client 1mtimeout server 1mstats enablestats uri /statsstats realm HAProxy\ Statisticsstats auth admin:packetfence
Next, uncomment the following line from /usr/local/pf/conf/iptables.conf
-A input-management-if --protocol tcp --match tcp --dport 1025 --jump ACCEPT
Now restart haproxy-portal and iptables in all nodes in order to complete the configuration:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service haproxy-portal restart# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service iptables restart
You should now be able to connect to the dashboard on each node using following URL : http://NODE_MANAGEMENT_IP:1025/stats
haproxy-db with port 1026 in haproxy-db.conf8.5. Configuration conflict handling
When modifying the configuration through the administration interface, the configuration will be automatically synchronized to all the nodes that are online. In the event that one or more nodes cannot be updated, an error message will be displayed with affected nodes.
A scheduled check runs on the management server (controlled through maintenance.cluster_check_interval) in order to validate if all servers are running the same configuration version.
When the failed node(s) will come back online, that scheduled check will ensure that the new configuration is pushed on the new node(s).
You can disable this check by setting maintenance.cluster_check_interval to 0 and restarting pfmon. In that case, you will need to manually resolve the conflict when the node(s) come back online by running /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/sync --as-master on the node you want to keep the configuration of.
General facts about conflict resolution:
- If the configuration is not pushed to at least half of the servers of your cluster, when the failed nodes will come back online, they will have quorum on the previous configuration and the one they are running will be pushed to all the servers.
- In a two node cluster, the most recent configuration is always selected when resolving a conflict.
- In a two node cluster, no decision is taken unless the peer server has its webservices available.
8.5.1. Going deeper in the conflict handling
The section below will explain with more details, the steps that are taken in order to take the decision of which server should be declared as the master when one or more servers have conflicting configuration version.
The first step is to get the configuration version from each server through a webservice call.
The results are then organized by version identifier. Should all alive servers run the same version, the state is considered as healthy and nothing happens.
Then, should there be more than one version identifier across the alive servers, the algorithm validates that there are at least 2 servers configured in the cluster. If there aren’t, then the most recent version is pushed on the peer node.
After that, the algorithm looks at which version is on the most servers. In the event that the dead servers are in higher number than the alive ones, the most recent version is taken. Otherwise, the version that is present on the most servers will be selected.
When pushing a version to the other servers, if the current server has the most recent version or is part of the quorum (depending on which push strategy was defined above), then it will be the one pushing the new configuration to the other servers. Otherwise, a webservice call is made to one of the servers running the selected version so that it pushes its configuration to its peers.
9. Additional Information
For more information, please consult the mailing archives or post your questions to it. For details, see:
- packetfence-announce@lists.sourceforge.net: Public announcements (new releases, security warnings etc.) regarding PacketFence
- packetfence-devel@lists.sourceforge.net: Discussion of PacketFence development
- packetfence-users@lists.sourceforge.net: User and usage discussions
10. Commercial Support and Contact Information
For any questions or comments, do not hesitate to contact us by writing an email to: support@inverse.ca.
Inverse (http://inverse.ca) offers professional services around PacketFence to help organizations deploy the solution, customize, migrate versions or from another system, performance tuning or aligning with best practices.
Hourly rates or support packages are offered to best suit your needs.
Please visit http://inverse.ca/ for details.
11. GNU Free Documentation License
Please refer to http://www.gnu.org/licenses/fdl-1.2.txt for the full license.
12. Appendix
12.1. Glossary
- 'Alive quorum': An alive quorum is when more than 50% of the servers of the cluster are online and reachable on the network (pingable). This doesn’t imply they offer service, but only that they are online on the network.
-
'Hard-shutdown': A hard shutdown is when a node or a service is stopped without being able to go through a proper exit cleanup. This can occur in the case of a power outage, hard reset of a server or
kill -9of a service. -
'Management node/server': The first server of a PacketFence cluster as defined in
/usr/local/pf/conf/cluster.conf. - 'Node': In the context of this document, a node is a member of the cluster while in other PacketFence documents it may represent an endpoint.
12.2. Setting the interfaces name on CentOS 7
On CentOS 7 you need to make sure that all the servers in the cluster use the same interfaces name. This section covers how to set the interfaces to the ethX format. Note that you can set it to the format you desire as long as the names are the same on all servers.
First, go in /etc/default/grub and add net.ifnames=0 to the variable: GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX.
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=centos/root rd.lvm.lv=centos/swap rhgb quiet net.ifnames=0"
Then regenerate the GRUB configuration by executing the following command:
# grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
Then, rename the network script of your management interface (eno16780032 in this example) to be in the ethX form (eth0 in this example)
# mv /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eno16780032 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
And rename the name of the interface in the following files (making sure you replace eno16780032 and eth0 by the appropriate values):
# sed -i.bak "s/eno16780032/eth0/g" /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0# sed -i.bak "s/eno16780032/eth0/g" /usr/local/pf/conf/pf.conf
Apply the last two steps for any other interface you have on your server. Keep in mind, you can use the PacketFence configurator to reconfigure them later as long as your management interface is correctly configured and is accessible on your network.
Now, reboot your server and when it finishes starting, your interfaces name should now be using the format ethX
12.3. Disabling IPv6 on CentOS 7
In order to disable IPv6 on CentOS, you must disable it in the Linux kernel.
Simply add the following line in /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
Then reload the file and reboot the server:
# sysctl -p# reboot
12.4. IP addresses in a cluster environment
12.4.1. DHCP and DNS services
In registration and isolation networks, each cluster member acts as a DHCP server. DNS configuration sent through DHCP contains physical IP address of each cluster member unless you enabled the option 'pfdns on VIP only' in 'System configuration → Cluster'
12.4.2. SNMP clients
If you use SNMP in a cluster environment, you will need to allow physical IP addresses of all cluster members to query your network devices (switches, WiFi controllers, etc.)
12.5. Performing an upgrade on a cluster
In this procedure, the 3 nodes will be named A, B and C and they are in this order in cluster.conf.
12.5.1. Backups
First, ensure you have taken backups of your data. We highly encourage you to perform snapshots of all the virtual machines prior to the upgrade. You should also take a backup of the database and the /usr/local/pf directory using:
# mysqldump --opt --routines -u root -p pf | gzip > /root/packetfence_db.sql.gz# tar -C /usr/local -czf /root/packetfence.tar.gz pf --exclude='pf/logs' --exclude='pf/var'
12.5.2. Disabling the auto-correction of configuration
The PacketFence clustering stack has a mechanism that allows configuration conflicts to be handled accross the servers. This will come in conflict with your upgrade, so you should disable it.
In order to do, so go in 'Configuration→System Configuration→Maintenance' and disable the 'Cluster Check' task.
Once this is done, restart pfmon on all nodes using:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pfmon restart
12.5.3. Upgrading node C
In order to be able to work on node C, we first need to stop all the PacketFence application services on it.
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pf stop
Due to disconnection issues with the systemd-logind service while yum is performing the update, you need to ensure the service is stopped disabled. The last command will then ensure your current process is removed out of the user-0.slice.
/usr/bin/systemctl stop systemd-logind/usr/bin/systemctl --now mask systemd-logind/usr/bin/systemctl daemon-reload/bin/bash -c "/usr/bin/systemctl status user-0.slice | /usr/bin/grep -E -o '─[0-9]+' | /usr/bin/sed 's/─//g' | /usr/bin/xargs -I{} /bin/bash -c '/usr/bin/kill -0 {} > /dev/null 2>/dev/null && /usr/bin/echo {} > /sys/fs/cgroup/systemd/tasks'"
Next, upgrade your operating system and PacketFence on node C:
# yum upgrade --enablerepo=packetfence
systemctl set-default multi-user.target) before rebooting and back to packetfence-cluster (systemctl set-default packetfence-cluster.target) after it boots up. This will make sure your services don’t start up after the reboot.Now, make sure you follow the directives in the upgrade guide as you would on a standalone server with the exception of the database schema updates.
12.5.4. Migrating service on node C
Node C should currently be running the latest version of PacketFence while A and B should still be running the older version and still be offering service. The database is also still being synced to node C via the packetfence-mariadb service.
Detach node C from the cluster
First, we need to tell A and B to ignore C in their cluster configuration. In order to do so, execute the following command on A and B while changing node-C-hostname with the actual hostname of node C:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/node node-C-hostname disable
Once this is done proceed to restart the following services on nodes A and B one at a time. This will cause service failure during the restart on node A
# For PF versions prior to 8.0/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service haproxy restart/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service keepalived restart
# For PF versions 8.0 and later/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service radiusd restart/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pfdhcplistener restart/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service haproxy-db restart/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service haproxy-portal restart/usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service keepalived restart
Then, we should tell C to ignore A and B in their cluster configuration. In order to do so, execute the following commands on node C while changing node-A-hostname and node-B-hostname by the hostname of nodes A and B respectively.
# systemctl start packetfence-config# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/node node-A-hostname disable# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/node node-B-hostname disable
Now restart packetfence-mariadb on node C:
# systemctl restart packetfence-mariadb
The commands above will make sure that nodes A and B will not be forwarding requests to C even if it is alive. Same goes for C which won’t be sending traffic to A and B. This means A and B will continue to have the same database informations while C will start to diverge from it when it goes live. We’ll make sure to reconcile this data afterwards.
Complete upgrade of node C
From that moment node C is in standalone for its database. We can proceed to update the database schema so it matches the one of the latest version. In order to do so, upgrade the database schema using the instructions provided in Upgrade guide.
Stop service on nodes A and B
Next, stop all application service on node A and B along with the database:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pf stop# systemctl stop packetfence-mariadb
Start service on node C
Now, start the application service on node C
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pf start
12.5.5. Validate migration
You should now have full service on node C and should validate that all functionnalities are working as expected. Once you continue past this point, there will be no way to migrate back to nodes A and B in case of issues other than to use the snapshots taken prior to the upgrade.
If all goes wrong
If your migration to node C goes wrong, you can fail back to nodes A and B by stopping all services on node C and starting them on nodes A and B
On node C
# systemctl stop packetfence-mariadb# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pf stop
On nodes A and B
# systemctl start packetfence-mariadb# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pf start
Once you are feeling confident to try your failover to node C again, you can do the exact opposite of the commands above to try your upgrade again.
If all goes well
If you are happy about the state of your upgrade, you can continue on the steps below in order to complete the upgrade of the two remaining nodes.
12.5.6. Upgrading nodes A and B
Due to disconnection issues with the systemd-logind service while yum is performing the update, you need to ensure the service is stopped disabled. The last command will then ensure your current process is removed out of the user-0.slice.
/usr/bin/systemctl stop systemd-logind/usr/bin/systemctl --now mask systemd-logind/usr/bin/systemctl daemon-reload/bin/bash -c "/usr/bin/systemctl status user-0.slice | /usr/bin/grep -E -o '─[0-9]+' | /usr/bin/sed 's/─//g' | /usr/bin/xargs -I{} /bin/bash -c '/usr/bin/kill -0 {} > /dev/null 2>/dev/null && /usr/bin/echo {} > /sys/fs/cgroup/systemd/tasks'"
Next, upgrade your operating system and PacketFence on each server:
# yum upgrade --enablerepo=packetfence
systemctl set-default multi-user.target) before rebooting and back to packetfence-cluster (systemctl set-default packetfence-cluster.target) after it boots up. This will make sure your services don’t start up after the reboot.You do not need to follow the upgrade procedure when upgrading these nodes. You should instead do a sync from node C on nodes A and B
# systemctl restart packetfence-config# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/sync --from=192.168.1.5 --api-user=packet --api-password=fence# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd configreload hard
Where :
- '192.168.1.5' is the management IP of node C
- 'packet' is the webservices username ('Configuration→Webservices')
- 'fence' is the webservices password ('Configuration→Webservices')
12.5.7. Reintegrating nodes A and B
Optional step: Cleaning up data on node C
When you will re-establish a cluster using node C in the steps below, your environment will be set in read-only mode for the duration of the database sync (which needs to be done from scratch).
This can take from a few minutes to an hour depending on your database size.
We highly suggest you delete data from the following tables if you don’t need it:
-
radius_audit_log: contains the data in 'Auditing→RADIUS Audit Log' -
ip4log_history: Archiving data for the IPv4 history -
ip4log_archive: Archiving data for the IPv4 history -
locationlog_archive: Archiving data for the node location history
You can safely delete the data from all of these tables without affecting the functionnalities as they are used for reporting and archiving purposes. Deleting the data from these tables can make the sync process considerably faster.
In order to truncate a table:
# mysql -u root -p pfMariaDB> truncate TABLE_NAME;
Elect node C as database master
In order for node C to be able to elect itself as database master, we must tell it there are other members in its cluster by re-enabling nodes A and B
# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/node node-A-hostname enable# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/node node-B-hostname enable
Next, enable node C on nodes A and B by executing the following command on the two servers:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/cluster/node node-C-hostname enable
Now, stop packetfence-mariadb on node C, regenerate the MariaDB configuration and start it as a new master:
# systemctl stop packetfence-mariadb# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd generatemariadbconfig# /usr/local/pf/sbin/pf-mariadb --force-new-cluster
You should validate that you are able to connect to the MariaDB database even though it is in read-only mode using the MariaDB command line. If its not, make sure you check the MariaDB log (/usr/local/pf/logs/mariadb_error.log)
Sync nodes A and B
On each of the servers you want to discard the data from, stop packetfence-mariadb, you must destroy all the data in /var/lib/mysql and start packetfence-mariadb so it resyncs its data from scratch.
# systemctl stop packetfence-mariadb# rm -fr /var/lib/mysql/*# systemctl start packetfence-mariadb
Should there be any issues during the sync, make sure you look into the MariaDB log (/usr/local/pf/logs/mariadb_error.log)
Once both nodes have completely synced (try connecting to it using the MariaDB command line), then you can break the cluster election command you have running on node C and start node C normally (using systemctl start packetfence-mariadb).
Start nodes A and B
You can now safely start PacketFence on nodes A and B using:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pf restart
12.5.8. Restart node C
Now, you should restart PacketFence on node C so it becomes aware of its peers again.
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pf restart
You should now have full service on all 3 nodes using the latest version of PacketFence.
Reactivate the configuration conflict handling
Now that your cluster is back to a healthy state, you should reactivate the configuration conflict resolution.
In order to do, so go in 'Configuration→System Configuration→Maintenance' and re-enable the 'Cluster Check' task.
Once this is done, restart pfmon on all nodes using:
# /usr/local/pf/bin/pfcmd service pfmon restart
12.6. MariaDB Galera cluster troubleshooting
12.6.1. Maximum connections reached
In the event that one of the 3 servers reaches the maximum amount of connections (defaults to 1000), this will dead-lock the Galera cluster synchronization. In order to resolve this, you should first increase database_advanced.max_connections, then stop packetfence-mariadb on all 3 servers, and follow the steps in the section 'Recovering from a split brain' of this document. Note that you can use any of the database servers as your source of truth.
12.6.2. Investigating further
The limit of 1000 connections is fairly high already so if you reached the maximum number of connections, this might indicate an issue with your database cluster. If this issue happens often, you should monitor the active connections and their associated queries to find out what is using up your connections.
You can monitor the active TCP connections to MariaDB using this command and then investigate the processes that are connected to it (last column):
# netstat -anlp | grep 3306
You can have an overview of all the current connections using the following MariaDB query:
MariaDB> select * from information_schema.processlist;
And if you would like to see only the connections with an active query:
MariaDB> select * from information_schema.processlist where Command!='Sleep';